Isothermal section of the Er–Ni–Sb ternary
system at 1073 K
Chem.
Met. Alloys 17 (2024)
5-12
L. ROMAKA, Yu. STADNYK, P. KLYZUB
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma17.0439
The interaction between the components in the
ternary system Er–Ni–Sb was investigated by X-ray diffraction, microstructural
analysis, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy in the full concentration
range at 1073 K. At this temperature, the Er–Ni–Sb system is characterized
by the existence of two ternary compounds: ErNiSb
(structure type MgAgAs, space group F-43m,
a = 0.62673(1) nm) and
Er5Ni2Sb (structure type Mo5SiB2,
space group I4/mcm, a = 0.7518(2),
c = 1.3287(6) nm). The
antimonide ErNiSb is characterized by a homogeneity
range that extends from 33 to 28 at.% Ni. The
binary compound (NaCl structure type) ErSb dissolves
up to ~14 at.% Ni, filling the vacant
8c site in the structure of ErSb by smaller Ni
atoms. The substitution-type solid solution Er5NixSb3-x (Yb5Sb3-type)
extends to about 6 at.% Ni.
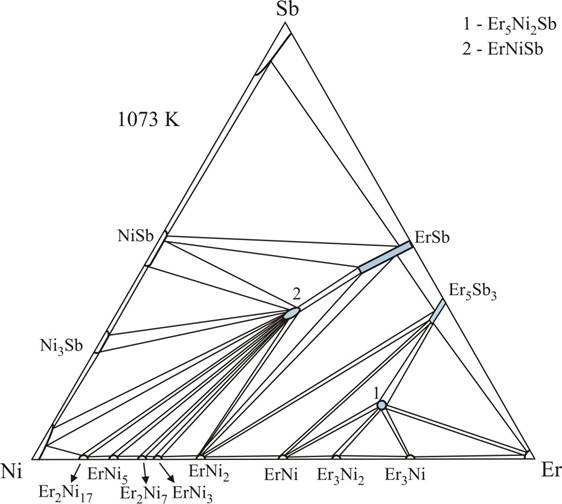
Isothermal section of the Er-Ni-Sb system at 1073 K.
Keywords
Intermetallics / Phase
diagram / X-ray diffraction / Scanning electron microscopy