The system Hf–Ga–Sn at
600ºC and the crystal structure of Hf5Ga1.24-0.52Sn1.76-2.48
Chem.
Met. Alloys 4 (2011) 175-187
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma4.0200
Iryna VOZNYAK, Yaroslav TOKAYCHUK, Roman
GLADYSHEVSKII
The isothermal
section at 600ºC of the phase diagram of the ternary system Hf–Ga–Sn
was constructed in the whole concentration range using X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray analysis. The binary gallides HfGa (structure type ThIn) and
Hf5Ga3 (Mn5Si3) dissolve up to 17 at.% Sn, forming solid
solutions characterized by constant Hf concentration. Based
on the binary stannide Hf5Sn3
(Mn5Si3) an interstitial solid solution up to 11.1 at.% Ga is formed. Other binary
compounds of the systems Hf–Ga and Hf–Sn do not
dissolve noticeable amounts of the third component. One ternary compound,
Hf5Ga1.24-0.52Sn1.76-2.48, with homogeneity
range 9 at.% Ga (Sn) is formed. Its crystal structure belongs to the
structure type Nb5SiSn2 (Pearson symbol tI32, space group I4/mcm), which is a
ternary variant of W5Si3. With increasing Sn content the unit-cell parameters within the homogeneity
range increase from a = 10.9154(8), c = 5.51311(15) Å
to a = 11.0203(7), c = 5.56591(16) Å.
The structure is built
up of two kinds of isolated column: face-sharing
square antiprisms GaHf8
and edge-sharing tetrahedra HfSn4.
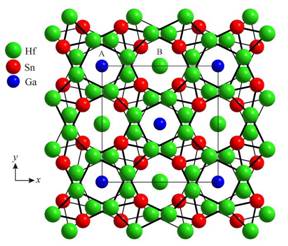
Projection of the structure of Hf5Ga1.24-0.52Sn1.76-2.48
along [001]
Keywords
Hafnium / Gallium / Tin / Phase diagram / X-ray
diffraction / Crystal structure / Solid solution