Adsorption-desorption properties of clinoptilolites and the catalytic
activity of surface Cu(II)–Pd(II) complexes in the reaction of carbon monoxide
oxidation with oxygen
Chem.
Met. Alloys 4 (2011) 213-218
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma4.0186
T.L. Rakitskaya, T.A.
Kiose, V.O. VASYLECHKO, V.Ya. Volkova, G.V. GRYSHCHOUK
Adsorption-desorption properties of
natural and acid-modified clinoptilolite (N‑CLI and H‑CLI,
respectively) with respect to Cu(II) and Pd(II) have been studied. It has been
found that an acid-thermal treatment (3M ÍNO3,
T = 373 K, 6 h) of N‑CLI
weakens the palladium bonding to the H‑CLI‑6 surface with a
fraction of weakly bound palladium(II) of 71.2 % and this alone determines
the activity of the K2PdCl4–Cu(NO3)2 / H‑CLI‑6 catalyst during carbon monoxide oxidation.
The bonds that copper(II) forms with the H‑CLI‑6 surface can
be divided into weak (30 %), medium-strength
(40 %), and strong (30 %) ones, however, the contribution of weakly
bound copper(II) amounts to only 4 % of the K2PdCl4–Cu(NO3)2 / H‑CLI‑6 catalytic activity.
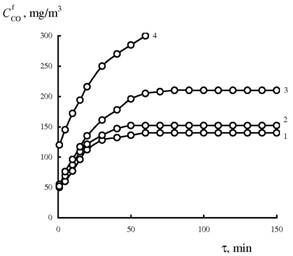
Time dependence of the activity of
K2PdCl4-Cu(NO3)2 / H‑CLI‑6 samples in the
carbon monoxide oxidation with oxygen under different conditions of copper(II)
desorption.
Keywords
Adsorption-desorption of copper(II)
and palladium(II) / Natural and acid-modified clinoptilolite / Catalyst for carbon
monoxide oxidation