Inhibition of aluminum
corrosion in acid solution by mono- and bis-azo naphthylamine dyes. Part 1
Chem.
Met. Alloys 4 (2011) 98-106
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma4.0168
E.M. MABROUK, H. SHOKRY, K.M.
ABU AL-NAJA
The effect of a series of mono- and bis-azo dyes derived from dihydroxynaphthalene on the
dissolution of aluminum in 2 M HCl solutions was
studied using weight loss, thermometry and galvanostatic
polarization techniques. The inhibition efficiency was found to increase with
increasing concentration of inhibitor to reach 97.86 % for 1×10-4 M. The
inhibition mechanism is discussed on the basis of adsorption of inhibitor
molecules on the metal surface. The inhibitors were adsorbed on the surface
according to the Temkin adsorption isotherm. The effect
of temperature on the corrosion inhibition of Al was studied and thermodynamic
functions for the dissolution and adsorption processes in the absence and in
the presence of the azo dyes were computed and
discussed. The results obtained from the chemical and electrochemical
measurements are in good agreement.
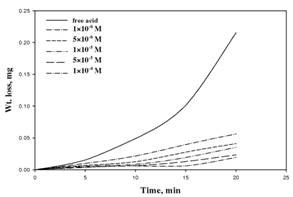
The weight loss vs. time for aluminum corrosion
in 2 M
HCl in the
presence of different concentrations of compound I.
Keywords
Naphthylamineazo dye / Aluminum / Inhibitors / Weight
loss / Thermometry / Polarization