Electrochemical behavior of
iridium and ruthenium in low-temperature melt electrolytes
Chem.
Met. Alloys 3
(2010) 42-48
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma3.0121
Anastasiya SAVCHUK, Nelly TUMANOVA,
Victor MALYSHEV
The electrochemical behaviour
of iridium and ruthenium in low-temperature melts based on carbamide
and acetamide was studied. It was shown that the
electrochemical dissolution of metals in the mentioned melts is accompanied by passivation and results in the formation of Ir(III)
and Ru(III) ammonia complexes, which are discharged
to the metal irreversibly in one step.
The stationary electrolysis of carbamide and acetamide melts leads to the deposition of metal on the
metallic substrates (Pt, Cu, Mo) in the form of
microcrystalline electroplating.
|
|
|
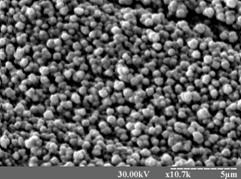
Мікрофотографія іридієвого
покриття з розплаву карбамід-NH4Cl , t 0 роб. = 1000 С.
Keywords
Iridium / Ruthenium / Kinetics / Electrolysis / Plating