The influence of methanesulfonate ions on physico-chemical
properties of lead dioxide
Chem.
Met. Alloys 14
(2021) 7-12
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma14.0413
Alexander VELICHENKO, Tatiana LUK’YANENKO,
Olesia SHMYCHKOVA, Pavlo DEMCHENKO, Roman GLADYSHEVSKII
The results of an
investigation of the influence of methanesulfonate
ions on physico-chemical properties of
electrochemically deposited lead dioxide are reported. It was possible to
synthesize high-quality films of up to
2 mm thickness, free from internal stress, with reliable adhesion
to the substrate in the current density range 2-180 mA∙cm-2.
Changes in the composition of the methanesulfonate
electrolyte or the deposition conditions affected the relative contents of the
α- and β-modifications of the dioxide. The main
difference, compared with lead oxides obtained from nitrate solutions, was the
significant amount of α-phase, which varied from 17 to 90%. The deposits
were well crystallized and contained smaller crystals.
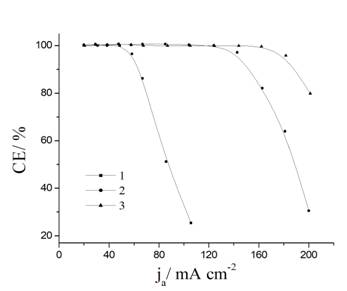
Current efficiency of PbO2 vs.
current density in different electrolytes: 1 – 0.5 M Pb(CH3SO3)2
+ 0.1 M CH3SO3H; 2 – 1.0 M Pb(CH3SO3)2
+ 0.1 M CH3SO3H; 3 – 1.0 M Pb(CH3SO3)2
+ 0.1 M CH3SO3H with stirring.
Keywords
Lead(IV) oxide
/ Methanesulfonate ion / Phase composition / Current
efficiency