The influence of surfactants
on nucleation and physico-chemical properties of lead
dioxide
Chem.
Met. Alloys 13 (2020)
29-35
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma13.0402
Tatiana
LUK’YANENKO, Olesia SHMYCHKOVA, Svitlana
ZAHORULKO, Alexander VELICHENKO
The results of
investigations concerning the early stages of electrocrystallization
of lead dioxide from surfactant-containing media and physico-chemical
properties of the composites involved are reported. The anionic surfactants
were sodium laureth sulfate and sodium dodecyl sulfate. It followed from the X-ray diffraction
patterns of the PbO2-C16H29SO6Na
samples that the surfactant additive had a significant impact on the structure
of the lead dioxide. The β (110)
and α (111) reflections had practically disappeared, and β (022)
had appeared. In fact, the composite material is β-PbO2 containing an X-ray amorphous phase of
the surfactant. On the contrary, the addition of C12H25SO4Na
to the nitrate electrolyte resulted in an almost twofold increase in the α-phase
content of the coating. The morphology and structure of the composite materials
differed significantly from those of lead dioxide. With an increase in the
surfactant content in the composite, there was a transition from large-grained
deposits to materials with submicron and nano-sized
crystals.
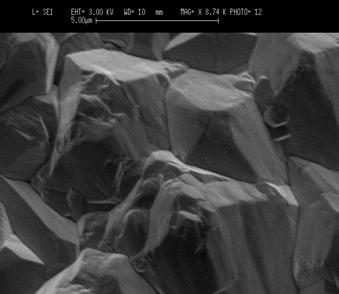
SEM micrograph of nondoped PbO2.
Keywords
Lead(IV) oxide
/ Nucleation / Morphology / Phase composition