Reciprocal K2TeI6
+ Rb2TeBr6 « K2TeBr6 + Rb2TeI6
system: phase relations, crystal and electronic structures
Chem.
Met. Alloys 13 (2020)
14-22
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma13.0400
I. Barchiy, O. Zubaka, E.
Peresh, V. Sidey, O. Kokhan, I. Stercho, A. Fedorchuk, M. Piasecki
The stability of the K2TeBr6(I6) and Rb2ÒåBr6(I6)
compounds with perovskite structures was assessed
within the idealized model of hard spheres (Goldschmidt’s rule). The
possibility of formation of solid solutions along sections of the reciprocal
system K2TeI6 + Rb2TeBr6 « K2TeBr6 + Rb2TeI6
was considered according to the quantitative criteria of Vozdvyzhensky.
The K2TeBr6–Rb2TeI6 system was
investigated by DTA and X-ray diffraction and the phase diagram was
constructed. The binary system is of the invariant eutectic type and
characterized by the formation of limited solid solutions. On the basis of
crystallographic data the bonds lengths in the crystal structures were compared
with the covalent and ionic radii of the atoms. The results showed that the
chemical bonds in the K2TeBr6(I6)
and Rb2ÒåBr6(I6) ternary compounds are of the
mixed (combined) type – iono-covalent with a larger
ionic component. The electronic structures of
the
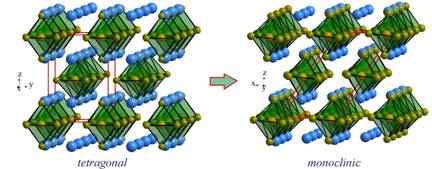
Transition from the tetragonal
structure of Rb2TeI6 to the monoclinic structure of K2TeBr6.
Keywords
Halide perovskite / Phase diagram /