Influence of Ho
substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of DyCu5Sn
Chem. Met. Alloys 12 (2019) 44-49
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma12.0394
A. ZELINSKIY, M. BOBNAR,
O. SICHEVYCH, L. AKSELRUD,
L. ROMAKA, R. GLADYSHEVSKII
Several samples from the homogeneity range of
the solid solution Dy1‑xHoxCu5Sn (x = 0-0.1) were prepared by
arc melting of the elements and annealed first at 1100 K and then at 870 K. The
crystal structure of DyCu5Sn was solved from single-crystal X-ray diffraction data, and Rietveld refinements of X-ray
powder diffraction data were carried out to analyze the evolution of the lattice
parameters in the solid solution. The Dy1‑xHoxCu5Sn
phase crystallizes with the structure type CeCu5Au (an ordered
variant of the CeCu6 type). The replacement of Dy
by Ho is accompanied by a decrease of the volume of the unit cell. The magnetic
behavior of the Dy1‑xHoxCu5Sn intermetallics was studied by magnetic susceptibility (χ) measurements in the temperature
range 1.8-400 K. Contrary to earlier reports a paramagnetic Curie
temperature of -3.9 K was found for DyCu5Sn, but the magnetic
behavior of the sample Dy0.9Ho0.1Cu5Sn, with a
critical temperature near 0 K, can be described by a quantum phase
transition associated with an antiferromagnetic
transformation.
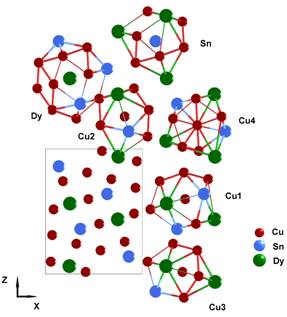
Projection
of the structure of DyCu5Sn onto the XZ plane and coordination polyhedra of the different atoms.
Keywords
Intermetallics / Crystal structure / X-ray
diffraction / Magnetic properties / Quantum phase transition