Nanocrystallization of iron-based amorphous alloys, influence of
magnetization in an alternating magnetic field
Chem.
Met. Alloys 11 (2018)
100-106
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma11.0373
Tetiana HULA, Oksana HERTSYK, Myroslava
KOVBUZ, Andrii Yakymovych,
Klaus W. Richter, Nataliia Pandiak
Nanocrystallization of iron-based amorphous alloys Fe82Nb2B14RE2, where RE = Y, Gd,
Tb, Dy, was studied by differential thermal analysis
(DTA) in the temperature range from 300 K to 1300 K. The structure
before and after the first stage of crystallization (~810 K) was checked
by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The measurements allowed determining the temperature and activation
energy of nanocrystallization. In addition, the
influence of magnetization in an alternating magnetic field on the nanocrystallization process in the amorphous alloy Fe82Nb2B14Gd2 was
studied. The
electrochemical changes caused by the alternating magnetic field were
investigated by potentiometry and voltammetry.
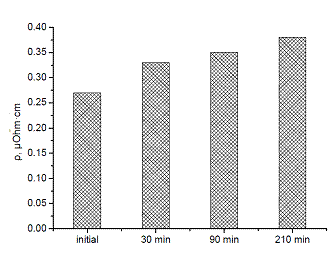
Resistivity of AMA Fe82Nb2B14Gd2,
before and after magnetization in AMF.
Keywords
Amorphous and nanocrystalline
alloys / Nanocrystallization / Differential
thermal analysis / Alternating magnetic field / Electrochemical properties