Effect of phase composition of
Ti–Zr–Mn–V alloys on the
hydrogen sorption properties
Chem.
Met. Alloys 11 (2018)
77-84
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma11.0371
V. DEKHTYARENKO, T. PRYADKO,
O. BOSHKO
The phase composition and crystal structures of
heterophase Ti–Zr–Mn–V alloys were studied by scanning electron microscopy
and X-ray diffraction. The structure of the as-cast and annealed alloys
consisted of a Laves phase and a bcc
solid solution. It is shown that the alloys interact with hydrogen at room
temperature and a pressure of 0.23 MPa with an
incubation period of 6-10 min and a duration of the
absorption process of 10 min. The resulting hydrogen sorption capacity was
more than 2 wt.%. Additional processing of the
obtained hydrides could increase the hydrogen sorption capacity.
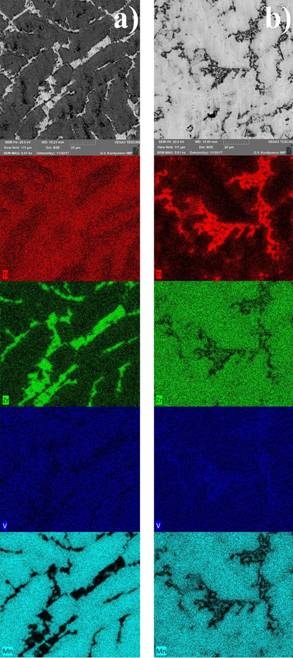
Microstructure and element distribution maps of
Ti19.8Zr34.8Mn43.3V2.1 (a) and Ti32.1Zr18.9Mn42.0V7.0
(b) as-cast samples.
Keywords
Hydrogen storage / Heterophase
alloy / Hydrides / Sieverts’ method / Hydrogenation