Thermal properties of Zn and Co(II) dihydrogenphosphate solid
solution
Chem.
Met. Alloys 10 (2017)
1-6
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma10.0333
N.M.
ANTRAPTSEVA, L.B. KOVAL, I.S. NOVAK
The
thermal properties of the solid solution Zn1-xCox(H2PO4)2·2H2O (0 < x < 1.00) were
investigated. It was found that the thermal stability of the dihydrogenphosphates correlates with the cationic
composition and increases with increasing cobalt(II)
content. The composition-dependent temperature range of formation and thermal
stability of the products of partial and complete dehydration were determined.
It was established that the final product of
dehydration is a cyclotetraphosphate
solid solution of composition (Zn1‑xCox)2P4O12,
0 < x < 1.00 (monoclinic, space group C2/c, Z = 4), which remains stable when heated to 900°C. A sequence
of solid-phase transformations taking place during the heat treatment is
proposed.
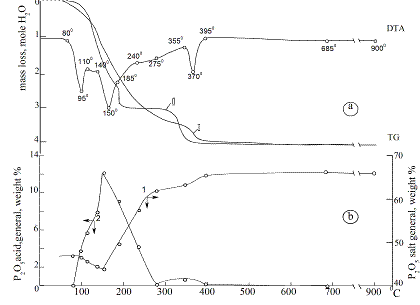
Thermal properties of Zn0.5Co0.5(H2PO4)2·2H2O.
Keywords
Phosphates / Solid solutions
/ Thermal properties