Hydrogen absorbing properties
of a Ti-Zr-Mn eutectic alloy
Chem.
Met. Alloys 1
(2008) 133-136
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma1.0044
V. IVANCHENKO, T. PRYADKO,
V. DEKHTYARENKO, T. KOSORUKOVA
Hydrogen storage properties of Ti-Zr-Mn eutectic alloys with the formula Ti0.475Zr0.3Mn0.225
were evaluated at ambient temperature and 565 °C using a Sieverts-type
device. The initial alloys were studied by means of SEM-EDS
technique, X-ray diffraction and DTA. The phase
compositions and the crystal structures of the hydrogenation products were
determined. The hydrogenation product obtained at room temperature consisted of
an e-hydride with a tetragonal crystal
structure of ThH2 type (a = 0.455
nm, c = 0.469 nm) and a
Laves phase-based hydride with MgZn2-type crystal structure (a = 0.5587±0.0005 nm, c = 0.9135±0.0007 nm) and had the composition 0.634(Ti0.64Zr0.29Mn0.066)H1.96 + 0.366(Ti0.18Zr0.32Mn0.5)H1.3.
The phase composition of the hydrogenation products obtained at 565 ۜ°C
was estimated to 0.55(Ti0.71Zr0.285Mn0.005)H1.85 + 0.45(Ti0.19Zr0.32Mn0.5)H1.35
and consisted of a d-hydride with a cubic crystal
structure of CaF2 type (a = 0.4597
nm) and a Laves phase-based hydride with MgZn2-type crystal
structure (a = 0.5598±0.0006 nm,
c = 0.9192±0.0008 nm).
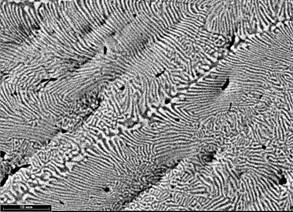
Microstructure of the 47.5Ti-30Zr-22.5Mn (at.%) eutectic alloy (electron back scattering image).
Keywords
Laves phase / Ternary alloy system /