Formation of microstructures
in Ti-Cr-V alloys with high hydrogen sorption capacity
Chem.
Met. Alloys 9 (2016) 158-163
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma9.0347
N.E. SKRYABINA, D. FRUCHART, N.A. MEDVEDEVA, P.
DE RANGO, A.A. MIRONOVA
TiVCr alloys known for their potentially large
hydrogen uptake were formulated as (TiCr1.8)100-xVx in order to quantify the impact of the vanadium
concentration. Parallel to this series of pure ternaries, a second one was
synthesized with 4 mol.% of Zr7Ni10 addition. Structural
investigation and electrochemical charging with hydrogen revealed a fair
dependence of the hydrogen uptake and hydride stability on the vanadium
content, but conversely different due to the presence of the Zr-Ni additive.
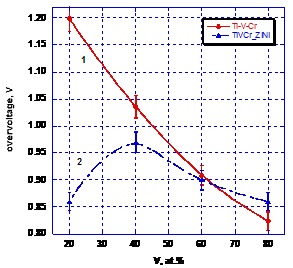
HER overvoltage for (TiCr1.8)100-xVx versus the V
content.
Keywords
B.c.c.
alloys / Zr-Ni additive / Microstructure / Hydrogen sorption / Electrochemical
properties