Ag3Ge2S5Br:
Synthesis, structure and ionic conductivity
Chem.
Met. Alloys 7 (2014) 139-148
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma7.0305
Mykola Moroz,
Pavlo Demchenko, Vitaliy Romaka, Roman Serkiz,
Lev Akselrud, Roman Gladyshevskii,
Oleksiy Mykolaychuk
A new compound, Ag3Ge2S5Br, was found on the intersection of the Ag3SBr–GeS2 and Ag2Ge2S5–AgBr polythermal cross-sections of the Ag2S–GeS2–AgBr system. The peritectic process L + GeS2 « Ag3Ge2S5Br takes place at T = 727 K. The crystal structure of Ag3Ge2S5Br was solved and refined using X-ray powder diffraction data: own structure type, space group P213 – b2a5, Pearson symbol cP44, Z = 4, a = 10.16702(7) Å, RI = 0.0395, c2 = 3.19. Ag3Ge2S5Br was also obtained in the glassy state. The charge and mass transfer of the crystalline and glassy phases was investigated by the dc probe method between 250 and 495 K. The samples are purely ionic (Ag+, Br–) conductors. The influence of lining of the transport channels by the halogens (Br–, I–) on the conductivity of crystalline (Ag3Ge2S5Br + 10 wt.% GeS2) and glassy (Ag3Ge2S5Br) samples was studied. Electronic structure calculations (FP-LAPW method) support the experimental results.
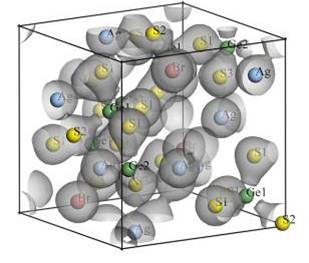
Isosurface
(ρ = 0.4 e/Å3)
of the electron
density in one unit cell
of Ag3Ge2S5Br
Keywords
Ag–Ge–S–Br / Phase formation / Crystal structure / Electrical conductivity / Superionics / DFT calculations