Study of the
kinetics and mechanism of the hydrogen evolution reaction on CeMe2Ge2 electrodes
(Me = Fe, Co, Ni)
Chem.
Met. Alloys 6 (2013) 113-120
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma6.0245
A.B. SHEIN, V.I.
KICHIGIN, M. KONYK, L. ROMAKA, Yu. STADNYK
The hydrogen evolution
reaction on the CeMe2Ge2 (Me = Fe, Co, Ni) germanides
in õ Ì H2SO4
+ (0.5-x) M Na2SO4
(x = 0.05-0.5) solutions has been studied using polarization and impedance
measurements. The conclusion has been made that hydrogen evolution on
the investigated materials occurs by the Volmer-Tafel
mechanism for a logarithmic isotherm of adsorption of atomic hydrogen.
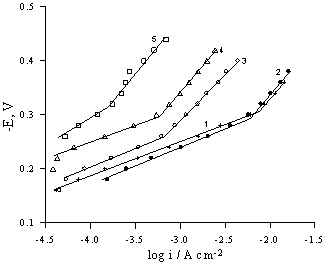
Polarization curves in õ Ì H2SO4 + (0.5-x) M Na2SO4
solutions.
1 – CeFe2Ge2;
2 – CeÑî2Ge2; 3-5
– CeNi2Ge2. For curves 1-3: x = 0.5, for 4: x = 0.15, for 5: x =
0.05.
Keywords
Intermetallic compound / Hydrogen evolution reaction / Hydrogen adsorption / Acidic
solution / Impedance