Dominant point defects in
germanium telluride crystals
Chem.
Met. Alloys 5
(2012) 155-159
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma5.0224
Dmytro
FREIK, Igor GORICHOK, Liubov YURCHYSHYN
The features of the experimental dependences of
the concentration of charge carriers on the temperature and chemical
composition of germanium telluride with NaCl-type structure at temperatures T = 550-850 K and concentrations of
excess tellurium XTe =
0.01-0.1 at.% Te are interpreted, and a crystal
chemical model is proposed for the defect subsystem. It was found that the
dominant defects under these conditions are doubly ionized metal vacancies,
which define the character of the dependences p(T), p(XTe). At temperatures above
750 K and for excess tellurium concentrations above 0.04 at.% Te, also antistructural chalcogen atoms have a
significant impact on the concentration of free holes. The concentrations of
other defects are much lower and do not affect the electrical properties of the
material.
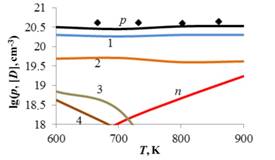
Dependence
of the concentrations of holes p,
electrons n and point defects in
β-GeTe crystals on temperature.
Keywords
Germanium
telluride / Electrical properties / Point defects