Electronic structure and magnetic properties of the Ce2MnGe6
compound
Chem.
Met. Alloys 1
(2008) 88-91
https://doi.org/10.30970/cma1.0010
A. SZYTUŁA, B. PENC, Yu. GORELENKO, M. KONYK, K. TOMALA, A. WINIARSKI
Magnetization, magnetic
susceptibility and X-ray photoemission measurements were performed on a Ce2MnGe6
polycrystalline sample. This compound crystallizes in an orthorhombic Ce2CuGe6-type
structure (space group Amm2). The Ce
atoms occupy two nonequivalent sites, while the Mn atoms only one site. The
magnetic data indicate that the compound is a ferrimagnet with the Curie
temperature TC = 150 K.
The magnetic moment determined from the magnetization curve measured at 2 K
increases from 1.9 μB for H
≈ 0 to 2.5 μB for H
= 50 kOe. Above TC the
reciprocal magnetic susceptibility fulfills the Curie-Weiss law with the
effective magnetic moment equal 5.3 μB. The valence band gives
a small peak at 0.3 eV below the Fermi level and a broad one with the maximum
at 2.1 eV, corresponding to the Mn 3d states. The structure of the Ce 3d5/2
and Ce 3d3/2 XPS spectra has been interpreted in terms of the Gunnarsson-Schönhammer
theory. Two final-state contributions of f1 and f2,
exhibiting a spin-orbit splitting of ΔSO = 18.7 eV, were
clearly observed. From the intensity ratio r = I(f2)/[I(f1) + I(f2)] =
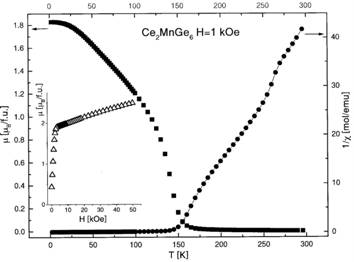
Temperature dependence of the magnetic moment and the
reciprocal magnetic susceptibility of Ce2MnGe6.
Keywords
Ternary rare earth germanides / Magnetic ordering / Electronic structure